Everyone has heard of aerobics – they’re the exercises you do when you want to strengthen your lung capacity, improve your overall fitness, and lose weight. The word “aerobic” is defined as being something relating to the intake of oxygen, and aerobic exercises are designed to help your body become more efficient in the absorption of oxygen.
When we talk about aerobic respiration, however, we aren’t simply talking about getting a good workout. Aerobic respiration is a biological function that all humans and a lot of other organisms experience. It’s a metabolic process that uses oxygen molecules to generate energy.
In addition to aerobic respiration, there is also anaerobic respiration, which is the conversion of sugars into energy in environments where oxygen isn’t present.
Learn more
How do scientists use models to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy?
If you were wondering how Gigi Hadid and Gisele Bundchen help us understand the process of photosynthesis, we’re sorry to inform you that we’re talking about different types of models!
There are all kinds of processes scientists use to better understand natural phenomena. Models are the tools they use to both learn about and explain different events, like photosynthesis.
Learn more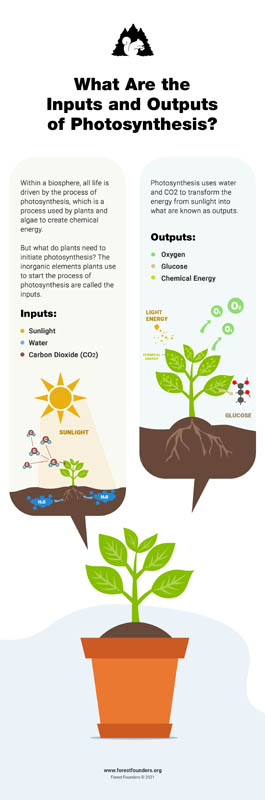
Every living thing needs energy to survive. Organisms get their energy from different food sources. Plants create their own food using energy from the sun, carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and water. Animals and insects eat plants and other animals for energy, and create waste that is used as food by bacteria and other microorganisms. This phenomenon is known as cycle matter and energy transfer, and it is best understood by studying food chains and food webs.
We’ve all heard of food chains — they’re the links that connect us to the plants and animals that we eat, the plants and animals they eat, and so on and on… all the way down to the tiniest insects and even beyond. Food webs, however, are a bit different.
Learn more
How does human activity affect the planet?
Everything we eat, wear, and use comes from natural resources that were grown or extracted. Some of these natural resources are renewable, which means that they either recur naturally, can be regenerated, or cannot be used up. natural resources include water, wind, sunlight, and vegetation. But other resources are non-renewable, like fossil fuels used to fuel cars and generate electricity.
When humans are careless about growing and extracting natural resources, it becomes difficult to access them, and the lack of access to life-sustaining resources can threaten our health. Over time, the inability to access natural resources causes us to suffer from economic difficulties. For example, if farmers can’t grow crops because their lands were damaged from bad farming practices, those farmers won’t be able to earn a living. This can lead to trouble when people become scared and desperate.
Learn more
Pollution occurs when the environment is altered by the release of natural or human-produced elements. These elements can be either physical matter or intangible matter. Pollution lowers the quality of the land, water, and air, and can even cause physical harm to humans, animals, and plants.
Pollution can be natural. For example, wildfires release ash and smoke that harm air quality. However, most of the pollution that causes the greatest amounts of harm is manmade, and comes from industrial processes, transportation, agriculture, and energy production.
Learn more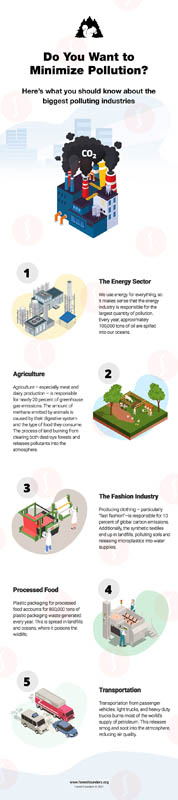
Air, sunlight, water, minerals, soil, plants, and animals are all examples of natural resources. Here is what you should know about conserving our natural resources for ourselves and future generations.
Are you familiar with the term “conservation?” When we conserve something, we are preserving it, rather than using it immediately or wasting it. In fact, “conserves” is another word for fruit jam, because people had to make jam out of their fresh fruit when it was first picked so that they could enjoy it for months, even years.
Learn more
Do you have trees where you live? Maybe you live close to public parks with lots of trees. Or maybe you live in a neighborhood where there are trees along the walkways. You might even live in a house with trees in your backyard.
Now, imagine there were no trees anywhere in your community. It would get extremely hot in the summer, because there are no trees to provide shade. Tree cover, also called tree canopy, is extremely important for helping neighborhoods stay cool, because trees block the sun’s harsh rays and prevent man made building materials like brick and concrete from absorbing and trapping heat.
Learn more
Reduce, reuse, recycle. You’ve probably heard those terms in commercials, but you might not have thought much about them. Don’t people reuse things? We don’t just throw away most things after only using them once, do we? And everyone recycles! (Don’t they?)
Most of us think we’re doing our part by putting bottles and cans into the recycle bin, but we don’t think about the amount of trash we throw away in a day. Did you know that each person in the U.S. throws away four pounds of trash every day? That’s a lot of trash!
Learn more
If you’ve ever had a messy room, you know that being disorganized can make it difficult to do things in a quick and easy – or efficient – way. The extra time you have to take to find the things you need can make you late for school or other activities, which means that you might not be at your best when you try to do your schoolwork or other tasks. Also – being in a messy room just doesn’t feel very good. (It sometimes doesn’t smell very good, either!) Cluttered rooms feel hotter and less comfortable, which can make it difficult to sleep very well.
In a way, the environment is similar. When we release pollutants by burning fossil fuels for electricity or transportation and create trash that ends up in the ocean and landfills, the environment becomes messy, and nature stops functioning as well as it would if the air was cleaner and if there wasn’t trash everywhere.
Learn more
The natural world is a complicated place. Every living thing relies upon something to survive, and every living thing provides a resource that helps the survival of something else. It’s like a chain where every plant and animal of every size is a link!
Living things are a part of the biosphere. All living things grow, survive, and reproduce because they exist with other living and non-things that help provide the food and other resources that sustain them. These are interdependent relationships. No living thing can exist without these interdependent relationships.
Learn more
When you feel physically ready and eager to do something, you might describe that feeling as being “full of energy.”
Well, whether it’s a person who feels energy or an object that uses energy, the term “energy” means the power to put something in motion. Energy is something that we use all the time in different ways. Chemical energy is a form of energy that is found in various elements. When we put gasoline in a car, the car uses the stored energy in the gasoline to create physical energy that makes the car perform. When we eat sugar and feel a bit hyper, we are receiving energy from the carbohydrates that are broken down into glucose in our bodies.
Learn more
There is nothing more important than good health. Good health means being in good physical condition and not being sick, but it can also mean having access to all of the different things we need to have a happy life. These might include good schools, fresh air, clean water, lots of space, and supportive friends and neighbors. All of these benefits help us take care of ourselves and our loved ones. While it might seem as though having all of these things depends upon living in a nice neighborhood and town, it’s really biodiversity that gives us the ability to enjoy all of these assets!
But why biodiversity?
We have learned about the food chain and how energy transfer and cycle matter are necessary in everyday life. Decomposers create the nutrients that feed producers and consumers, which allows the circle of life to function. So, if there were no decomposers depositing nutrients into the soil, then plants couldn’t grow, and animals and insects wouldn’t have anything to eat. We depend upon all of these different plants and animals to perform their jobs so that there is a thriving environment that supports everything. It’s biodiversity that gives us the trees, plants, animals, insects, and lots of other resources we need to make the things we use every day.
Learn more
When we use the phrase “climate change,” what exactly do we mean?
Global climate change is a description of a widespread rise in temperatures around the world over the course of years and even decades. The global climate has risen because of a combination of natural events and human impact, but it is the human impact that has driven the biggest changes to the climate over the past hundred years. Human interference has caused such a significant effect on climate because so many of our lifestyle behaviors are dependent upon activities that emit harmful greenhouse gasses. From driving to work to using a smartphone, most of our activities affect climate.
Learn more
Climate change is a phrase you’ve probably heard a lot in school or on the news. But what is it, really?
Seasons change, and the weather changes all the time. Why is climate change different?
Climate change is the overall change in the planet’s weather systems over the course of many years. When we discuss recent climate change, we are talking about the fact that scientists have discovered gradual warming of the planet to the hottest temperatures ever recorded in the last two decades.
Learn more
Did you know that if you were to count all of the things in your room that weren’t made from a natural resource, you wouldn’t even get to number one?
Everything on Earth depends on natural resources. Natural resources are the things that nature produces that allow us to survive. These include air, sunlight, water, soil, rocks, vegetation, fuels, and animals. All of these resources together help to create the diversity of life on Earth.
Learn more
When was the last time you went outside?
You probably go outside every day. In fact – practically everyone goes outside every day! It’s a completely normal, not-particularly-exciting part of life (except when you’re going someplace awesome, like to the beach to snorkel or the mountains to snowboard, of course). However, even doing regular things outside like riding your bike or cutting the grass has an effect on the environment.
Learn more
Do you know what an ecosystem is?
An ecosystem is all of the living and non-living natural elements in a specific location. Every place has its own ecosystem. There is a distinct ecosystem in the region where you live that is different from one even a few miles away.
Learn more
You’ve probably seen plenty of worms. If you’ve seen a worm in a pile of leaves on your lawn, that worm was probably eating those dead leaves. After that worm has broken down those leaves, it releases matter into the soil in the form of nutrients. The surrounding grass then absorbs those nutrients through its root system. When the grass grows, it attracts insects that eat grass, such as beetles and grasshoppers. Birds then might eat the insects. All of these creatures feeding on different things in their ecosystem are examples of cycle matter and energy transfer. Matter is cycled and recycled, and cellular energy is transferred. It’s how all living things survive – including humans!
Learn more
What does carbon credit trading mean? It’s complicated, but here’s an example that might help you understand the process.
Let’s say it’s your job to cook dinner for your family. The last time you cooked, you used up every pot, pan, and dish in the kitchen, and it took more than an hour to wash up afterward. Because the whole process used lots more time and work than necessary, the next time you cook dinner, you decide to organize your time and equipment so that you don’t have to use as much energy. Maybe instead of using a different bowl for every step in the cooking process, you only use one. Maybe you tidy up as you go, so you don’t have a big mess at the end. This is called improving your efficiency, and it not only saves you time, but it also saves labor and even soap and water since you aren’t washing as many dishes.
Learn more
Forests are magnificent places – they’re filled with so many fascinating animals and plants that researchers are discovering new ones every two days! The world’s forests keep the planet cool, cause precipitation (rain), and purify our air and water. Forests are so important to humans and animals that if all the forests suddenly disappeared, the earth would become uninhabitable, meaning that the remaining life on the planet might not be able to survive.
So, who is in charge of the forests?
Learn more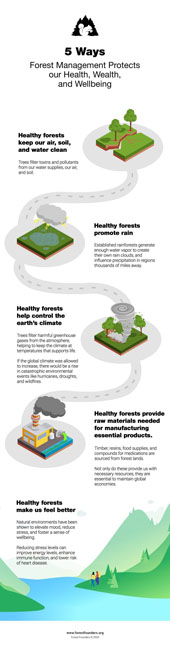
How much do you know about forests? You probably know them as mysterious green places where you can find lots of animals and plants. You might have even read about people living in or near forests, like in Laura Ingalls Wilder’s Little House in the Big Woods and J.K. Rowling’s Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone. But forests are much more than beautiful, tree-filled places where people (and sometimes wizards) have adventures – they also help people and animals everywhere have clean air to breathe and clean water to drink.
Learn more
When you think of invaders, you probably think of big armies that flood into a place and frighten and even harm everyone that already lives there. But did you know that some of the pretty trees and flowers that you see in people’s gardens or even on the side of the road are invaders that are harming the naturally occurring plants and animals that had been there previously? These invaders are non-native plants, and while they can be beautiful to look at, they can be dangerous to wildlife and – over time – humans.
Learn more