Forests are magnificent places – they’re filled with so many fascinating animals and plants that researchers are discovering new ones every two days! The world’s forests keep the planet cool, cause precipitation (rain), and purify our air and water. Forests are so important to humans and animals that if all the forests suddenly disappeared, the earth would become uninhabitable, meaning that the remaining life on the planet might not be able to survive.
So, who is in charge of the forests?
You might think that nature is in charge of itself, and it largely is. Mother nature has a remarkable way of regenerating and responding to major changes, environmental problems, and even human mistreatment. Unfortunately, sometimes those responses aren’t good for either the survival of the animals and the plants in the affected ecosystem, or for the humans that need natural resources. When human interference harms forests, forests can become susceptible to fires, diseases, and invasive species that can cause long-term harm. When forest systems are damaged, those forests must be restored to their previous health and not allowed to succumb to human negligence. This is why forest management services are so important.
Forest management is a critical resource for the protection and appreciation of forests and their wildlife. In addition to ensuring that forests stay healthy and vital, forest management services and processes aid in the recreational aspects of forest land, so that people can learn about, use and enjoy forests respectfully and sustainably.
While forest management is based in science, in practice, forest management is an active process that uses the best strategies and principles for long-term forest protection. These processes involve the following factors:
- Silviculture: We need to understand the needs and the biology of all of the forest trees to better protect them. Silviculture is a system wherein forest vegetation growth, quality, composition, and density are controlled. While this is largely for the purpose of maintaining and preserving forests for timber production, silviculture also helps to ensure forest adaptability to different environmental concerns.
- Forest Protection: Forest protection is largely dedicated to preventing and alleviating man-made forest damage, including wildfires, agricultural encroachment, logging, the spread of disease, pollution, and invasive plant and insect species.
- Watershed Management: Watershed management is the study, maintenance, and supervision of waterways and wetlands (rivers and lakes) to ensure sufficient water supplies, proper water quality management, the control of stormwater runoff, establish and maintain aquatic habitat protections, and to settle water rights, among other responsibilities. This process makes sure that there is plenty of clean water for everyone and everything.
- Wildlife Preservation: There are countless animal species in the world’s forests, and every one of them deserves a healthy environment and a chance to survive. Wildlife preservation is a key factor in forest management; the biodiversity of forest lands is very important to forest protection and long-term health.
Successful forest management means making sure forests are protected so that the environment stays healthy and that forests are always available for important resources. This means simultaneously ensuring forest lands are able to produce the raw materials necessary for the production of commercial goods while remaining vital and healthy ecosystems that survive and thrive for future generations.
Why Forest Management is Important
Forest management is an essential service for the protection of forests, but why is it important to protect forests in the first place?
Forests are critical habitats for humans and wildlife alike. While more than 300 million people live in and rely upon the health and viability of forest woodlands, the health of forests impacts all people, regardless of how close they live to forest lands, in the following ways:
Forests provide clean air.
In addition to releasing oxygen into the environment, forests absorb harmful CO2 from the atmosphere during the process of photosynthesis. A single mature tree can produce a full day’s worth of oxygen for up to 10 human beings.
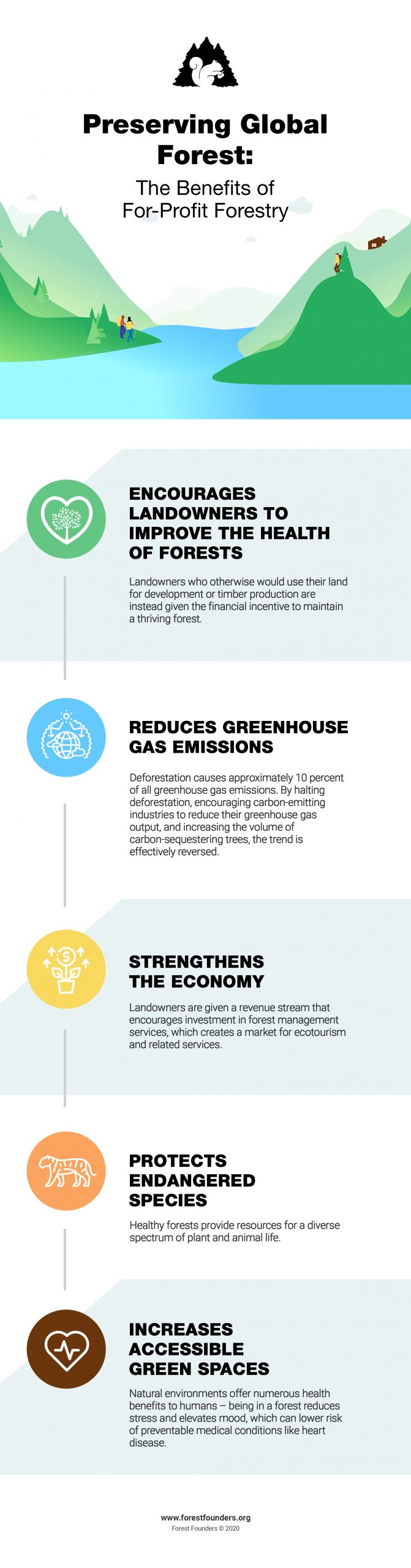
Forests control climate.
By absorbing harmful greenhouse gasses released by industrial production, air travel, automobiles, and the power supply, forests can help to control the climate. Global warming, if left alone, will make the earth too hot for a wide variety of plant and animal species, increase the frequency of extreme weather events like hurricanes, increase the acidity of oceans, and make growing and raising food extremely difficult.
Forests create rain. Literally.
Amazon rainforests have been shown to create their own water vapor through a process known as transpiration. The underside of broad leaves from rainforest trees release sufficient moisture to create low-hanging rainclouds over the Amazon forests. It is believed that Amazon rainforests create atmospheric events that encourage rainfall as far away as North America.
Forests replenish groundwater.
In addition to essentially creating rain, forests enable water absorption into the groundwater system, effectively replenishing aquifers in a process known as groundwater recharge. Groundwater is critical for creating sufficient drinking water reserves for the local populations.
Forests are natural air, soil, and water filters.
Established forests can help clear pollutants from the air, water, and soil. They absorb CO2 and other emissions from the environment, clear toxins – including lead – from soils through the process of phytoremediation, and filter sediments from the water before it reaches aquifers. In urban areas, trees have been credited with saving approximately 850 lives per year by removing harmful pollutants from the environment.
Forests give us valuable resources – including new potential medical cures.
Forests give us important medicines that can treat and even cure dangerous diseases. From cancer-fighting compounds found in rainforests to properties in cedar needles that fight severe antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections, forests are an incredibly rich resource for preserving our health.
Forests enhance feelings of wellbeing.
Walking through forests makes us feel better! Forests and natural environments trigger an emotional response called biophilia, which causes a desire to explore, learn, and communicate with nature. Moreover, natural environments have been associated with lowered stress responses and enhanced feelings of happiness and wonder.
Forest Founders was conceived to help restore and preserve the world’s forests. To participate in initiatives supported by Forest Founders, please visit the Forest Founders information page.